Content class definition configuration
Configuring a content class to be exportable is a two steps procedure:
Step 1: Knowing if a class is exportable or not
Go to the «Setup» tab in your Administration Interface, and select «Classes» in the left menu. Here you may choose any content class you want and go to its definition.
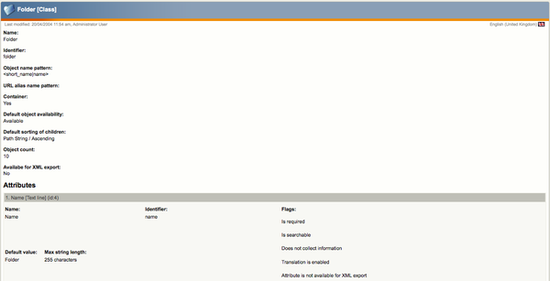
For example, for the «folder» content class you should get the following screenshot :
Below the «Object count» line you should see the following title «Available for XML export». If the value of this attribute is «No» then you will not be able to export any content of this content class. For each attribute you can also choose whether it is exportable or not. In the above screenshot we see that the «Name» attribute is not available for XML export.
Note that if a content class is not defined as available for XML export then none of its attribute will be available for XML export.
Step 2: Making a class available for XML export
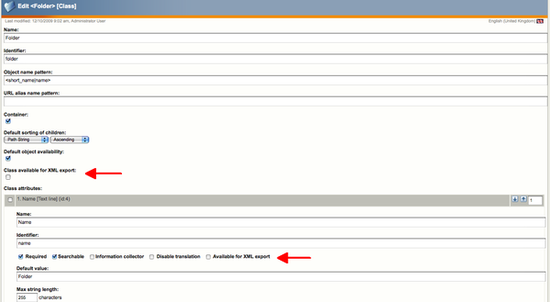
Because not all content classes or all their attributes need to be exportable, users themselves can decide which classes they want to be able to export. The only thing users have to do is to edit the content class by clicking on the «Edit» button available at the bottom of the content class definition. You should get something like this:
Click on the «Class available for XML export» check-box first and then, for each attribute you want to export, click on the «Available for XML export» check-box. Once you have defined the content class and all the attributes you want to export, just click on «OK» or «Apply» to save your changes.
List of available datatypes
Below you will find the list of eZ Publish datatypes that are currently available for XML rendering in eZ XML Export. By clicking on the datatype name you will be redirected to the datatype reference page. By clicking on the eZ Publish internal name you will be redirected to the XML schema definition of that datatype.
| Datatype name | eZ Publish internal name | Handeled in eZXMLexport |
|---|---|---|
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| Float |
yes |
|
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| ezinisetting |
no |
|
| ezinteger |
yes |
|
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| Matrix |
yes |
|
| yes |
||
| ezmultioption |
no |
|
| ezmutlioption2 |
no |
|
| ezmultiprice |
no |
|
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| ezoption |
no |
|
| ezpackage |
no |
|
| ezprice |
no |
|
| Product |
ezproduct |
no |
| Range |
ezrange |
no |
| no |
||
| Subtree |
ezsubtree |
no |
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| yes |
||
| ezuser |
no |
|
| yes |
Restrictions
Restrictions on a few datatypes like ISBN, URL or email are defined globally in the XML Schema because it is not possible to define restrictions directly in complex types. The export also adds a few meta data for each exported content object:
- creation date
- modification date
- language code in ISO format
- published version number
- creator identifier
<xs:attributeGroup name="objectinfo"> <xs:attribute name="creation_date" type="xs:dateTime" use="required"/> <xs:attribute name="modification_date" type="xs:dateTime" use="required"/> <xs:attribute name="publication_date" type="xs:dateTime" use="required"/> <xs:attribute name="lang" type="xs:string" use="optional"/> <xs:attribute name="version" type="xs:integer" use="required"/> <xs:attribute name="creator_id" type="xs:integer" use="required"/> </xs:attributeGroup>
Ester Heylen (05/11/2009 3:00 pm)
Geir Arne Waaler (22/10/2010 12:13 pm)

Comments
There are no comments.